

Are you making one of the top 5 mistakes that plague wholesale
distributors? Download our free eBook to find out.

Carlos LopezAdministration Manager


Brent EdwardsGeneral Manager
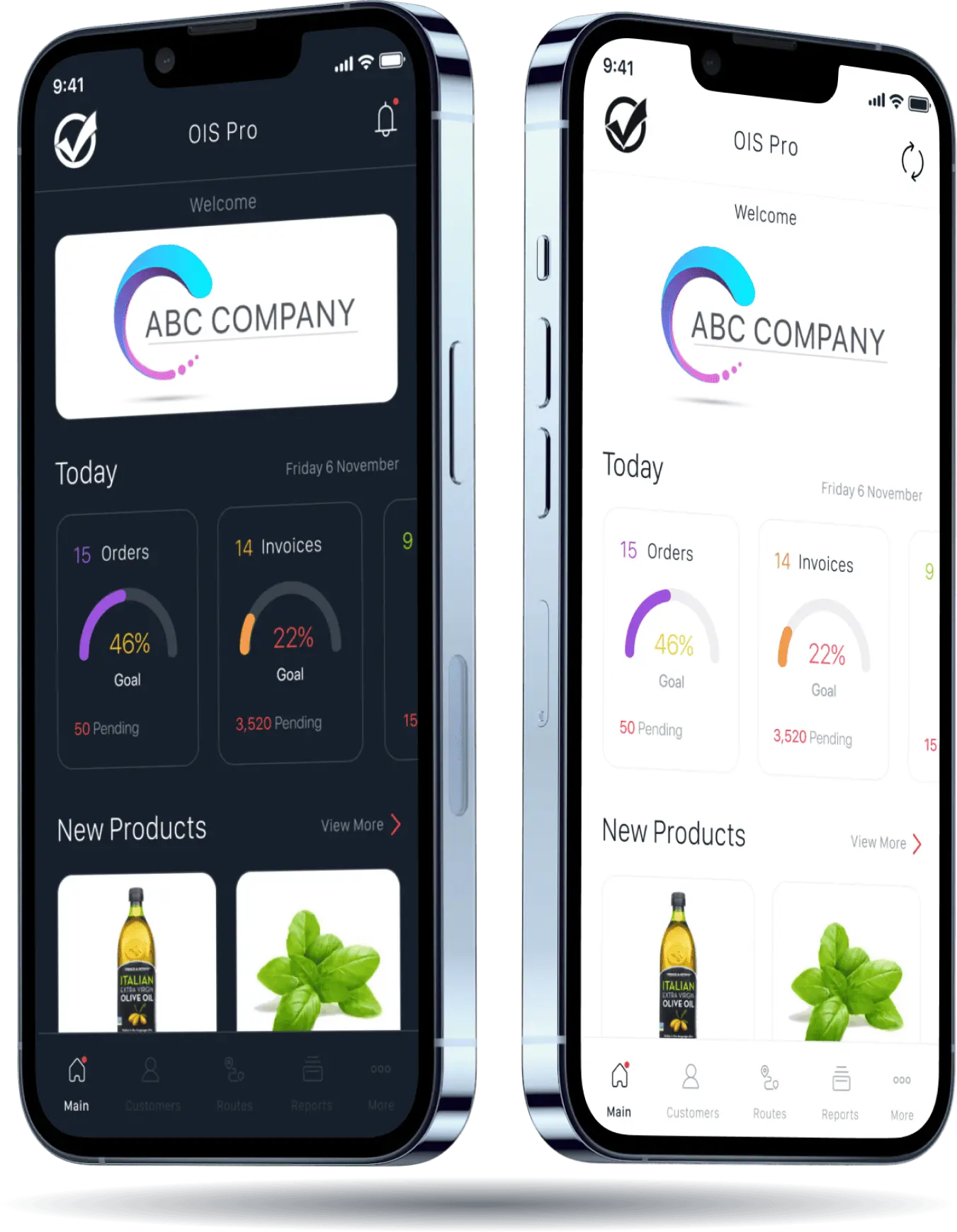
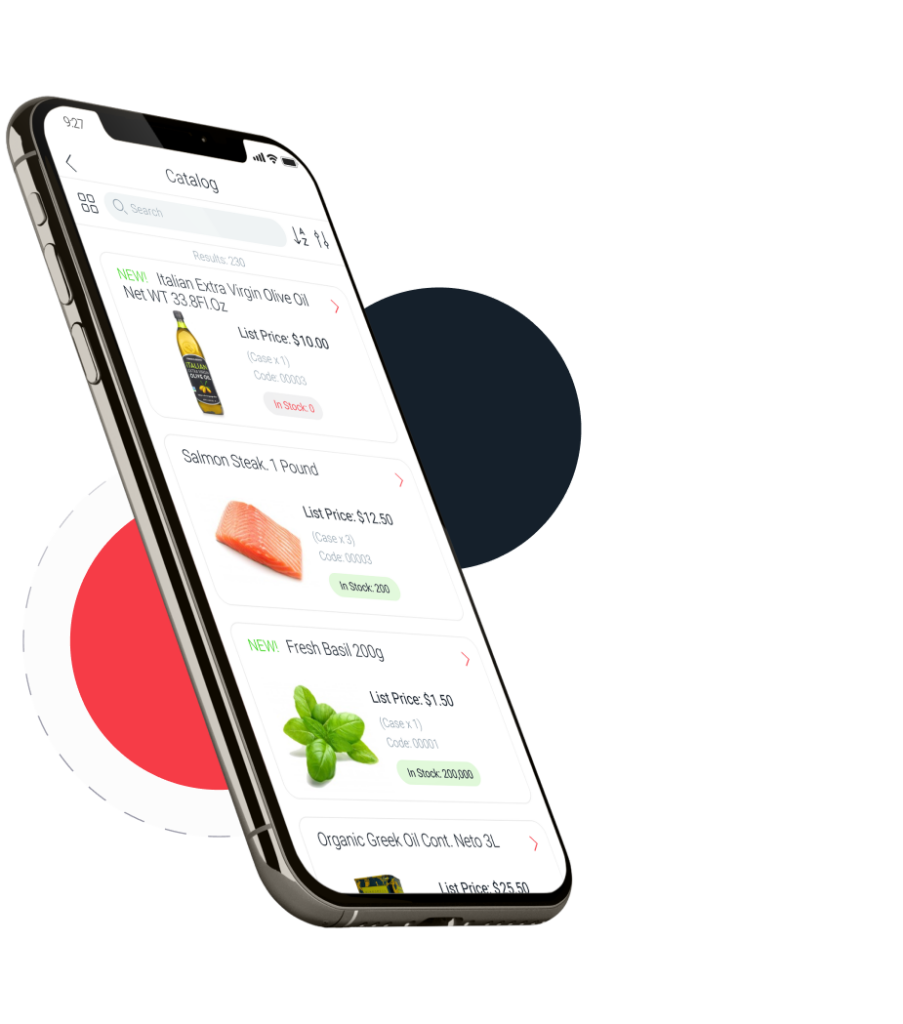
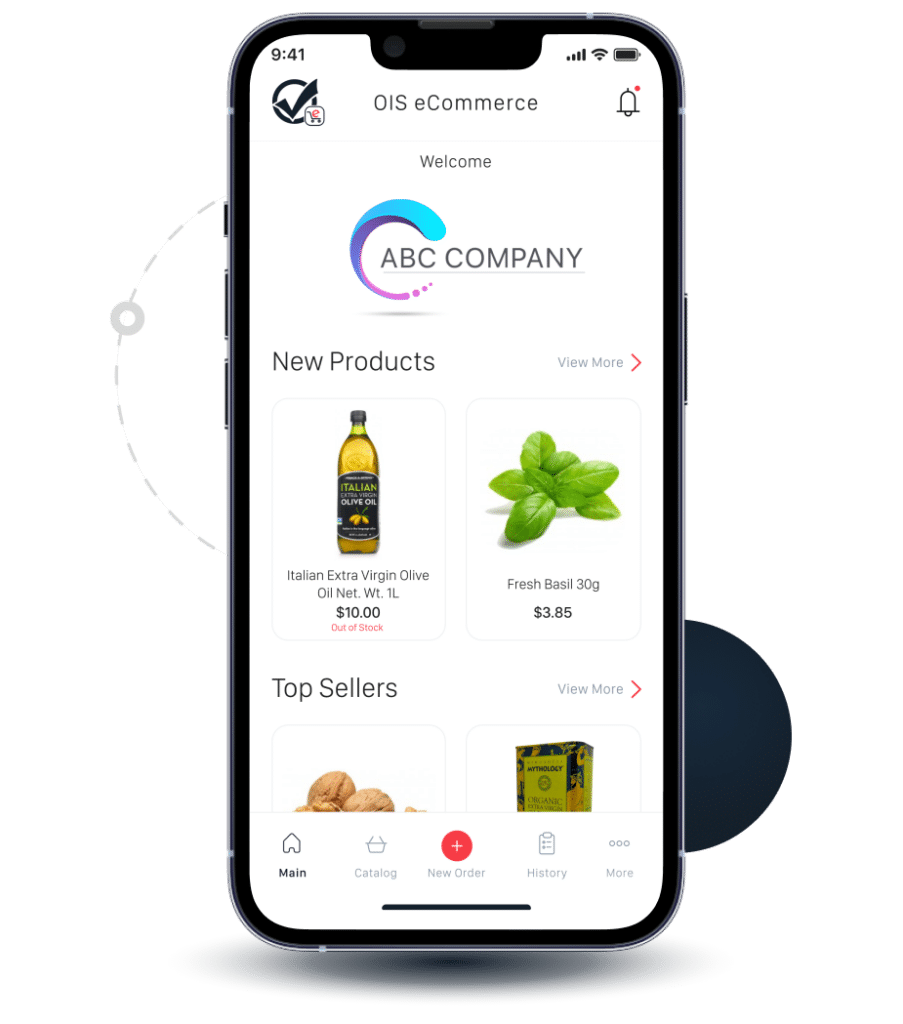
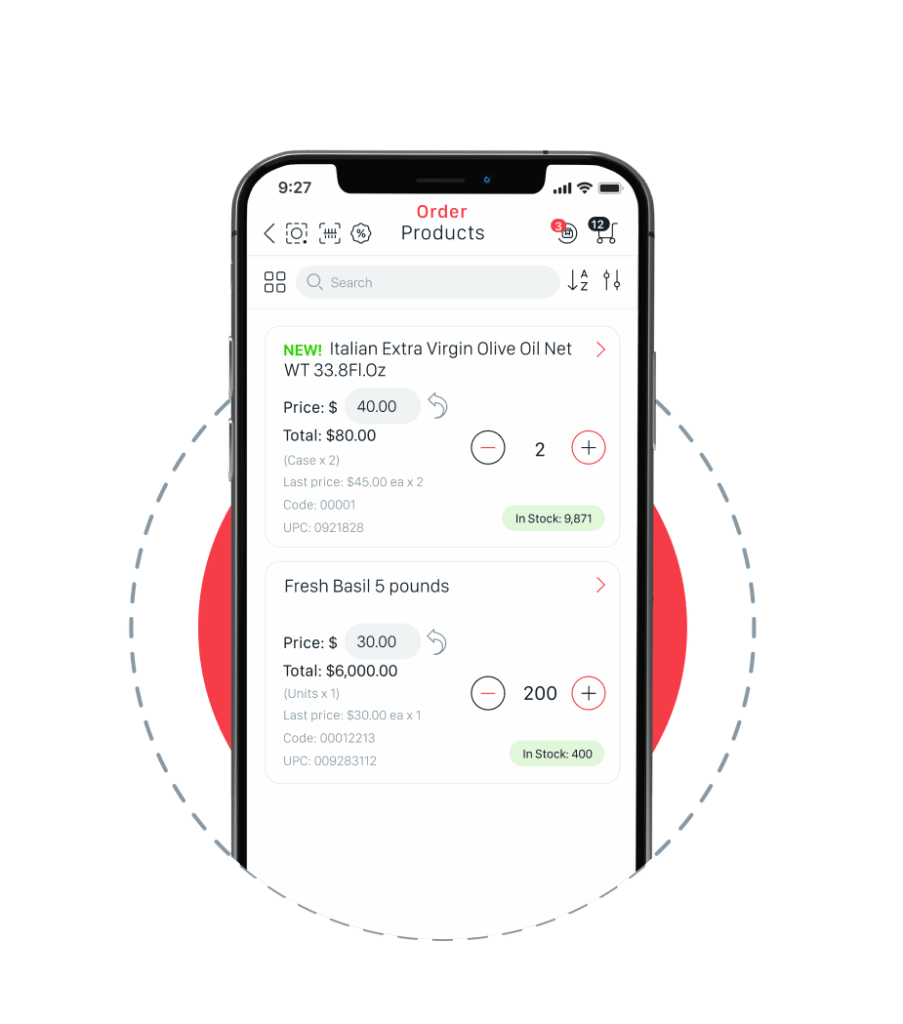
Impress customers by offering an app that’s easy-to-use, makes placing orders a breeze and sells 24/7. B2B eCommerce ordering increases efficiency, cost savings, improves accuracy and customer relationships.

Zain ManshaOwner
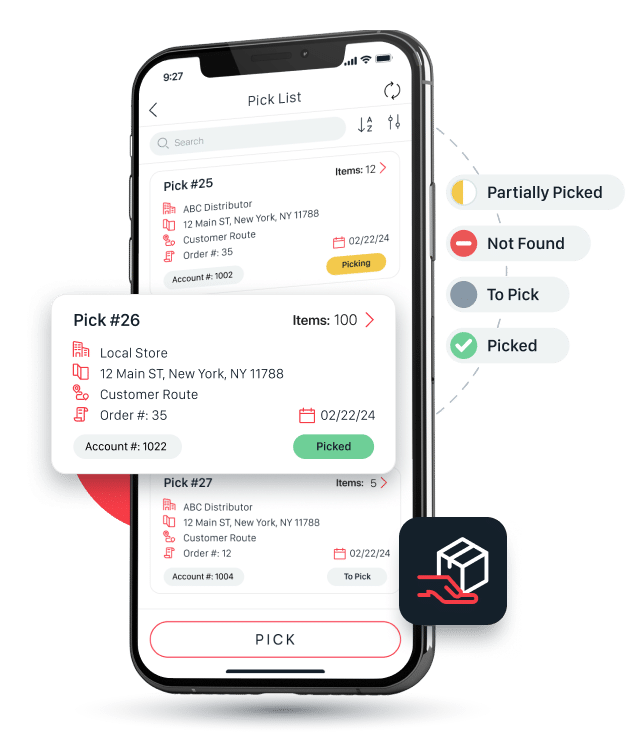
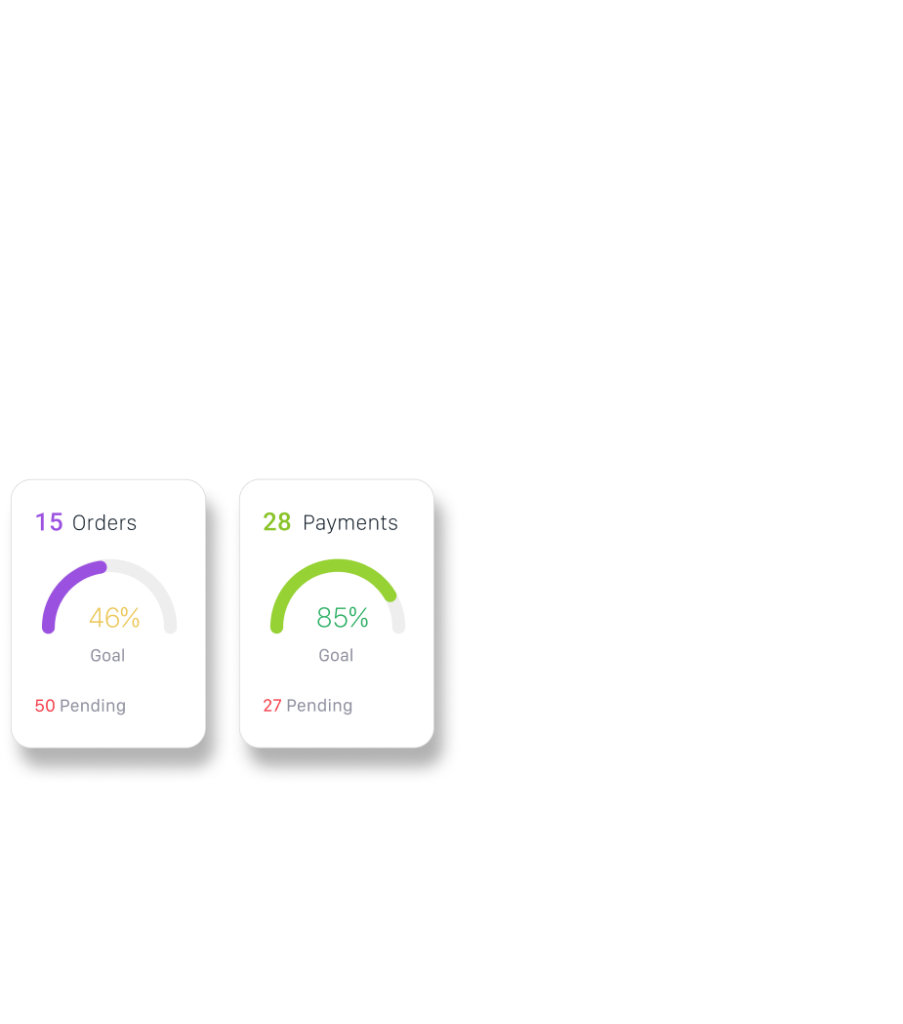
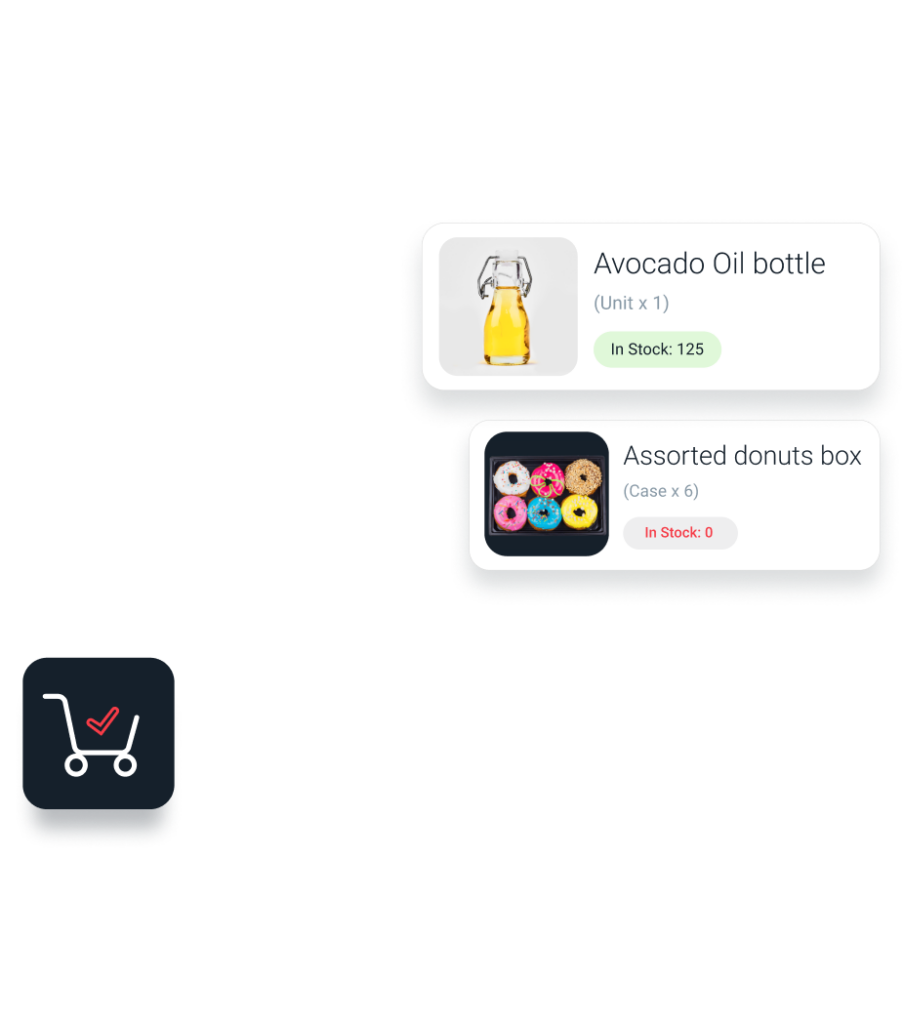
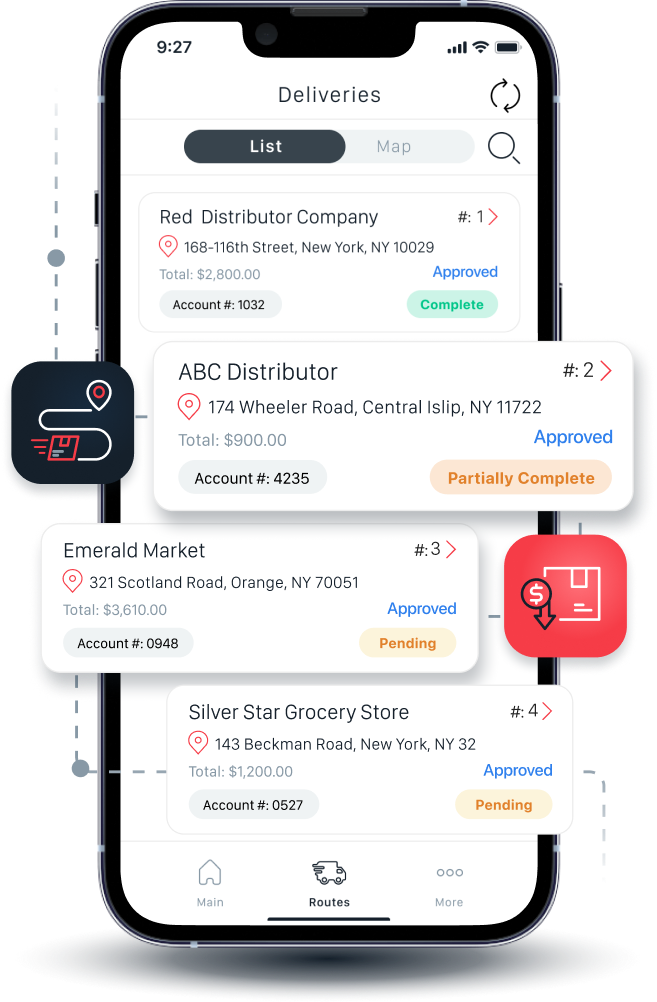
Automate warehouse order picking workflows with OIS Inventory, saving time on each pick while creating greater efficiency, and more importantly, eliminating errors.

Claudia SolartePresident

Armando EsquivelOwner


Paola VasquezManager




Ron ClagnazSales Manager











This exclusive eBook is packed with real-world, data-driven concepts
that can help maximize your store visits and double your sales.
Get it for FREE – Today!

This exclusive eBook is packed with real-world, data-driven concepts that can help maximize your store visits and double your sales.
Get it for FREE – Today!