How to Set Prices for Wholesale Distributors
 Determining the best distributor pricing strategy for a B2B wholesale distributor can be difficult, whether you are a new wholesale consumer-packaged-goods (CPG) brand just getting started or an established brand launching a new product line.
Various mathematical formulas are used to calculate a product’s price, margin, markup, markdown, profitability, and sales history. Fortunately, there are only a few things you need to know when pricing products for wholesale.
In this blog post, we’ll review a few of those formulas as well as some steps you can take to develop successful wholesale pricing strategies.
But first, let’s clarify what wholesale pricing is and how it differs from retail pricing.
Determining the best distributor pricing strategy for a B2B wholesale distributor can be difficult, whether you are a new wholesale consumer-packaged-goods (CPG) brand just getting started or an established brand launching a new product line.
Various mathematical formulas are used to calculate a product’s price, margin, markup, markdown, profitability, and sales history. Fortunately, there are only a few things you need to know when pricing products for wholesale.
In this blog post, we’ll review a few of those formulas as well as some steps you can take to develop successful wholesale pricing strategies.
But first, let’s clarify what wholesale pricing is and how it differs from retail pricing. Table of Contents
- Wholesale Pricing Definition
- What’s the Difference Between Wholesale & Retail Pricing?
- Wholesale Price Optimization for Retailers
- How is Wholesale Pricing Calculated / How to Calculate a Price for Wholesale Distributors
- CPG Wholesale Pricing
- 2 Types of Formulas to Calculate Wholesale Price
- Distributors Pricing: The Art of Balancing Profitability and Competition
- Conclusion
Wholesale Pricing Definition
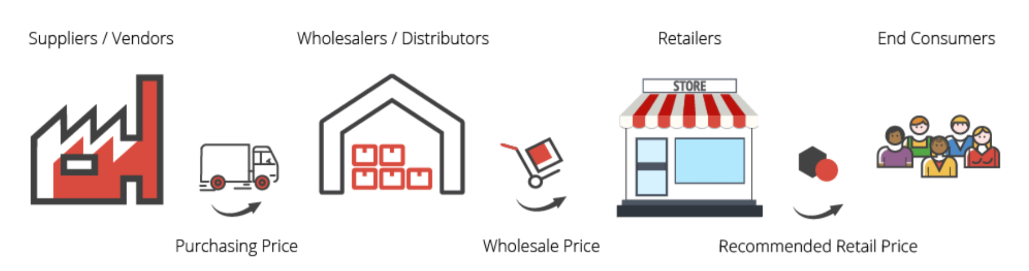
The wholesale price is the cost at which goods are sold by manufacturers or wholesalers to retailers, resellers, or distributors. This price is typically lower than the retail price because it is intended to allow the buyer to purchase goods in large quantities and resell them at a profit. Wholesale prices are often determined based on the cost of production, including raw materials, labor, and overhead, as well as a markup to ensure a profit for the wholesaler. By offering lower prices for bulk purchases, wholesalers encourage retailers to buy larger quantities, which helps streamline distribution and increase overall sales volume. Wholesale prices can also vary significantly depending on the product category, as different categories have unique cost structures and market expectations.
The goal of wholesale pricing is to make a profit by selling consumer goods at a higher price than it costs to manufacture them. For example, if making one product costs you $10 in labor and materials, you could set a wholesale price of $20, giving you a $10 per unit gross profit.
What’s the Difference Between Wholesale & Retail Pricing?
When compared to wholesale prices, retail prices are relatively high. This is because retail profit margins must typically be higher to account for expenses and operating costs such as advertising and marketing, rent, staff salaries, utilities, and so on.
Wholesale businesses have lower operating costs than retail businesses because they require less skilled labor, marketing efforts, physical storefront maintenance, and so on. As a result, wholesale pricing is founded on the idea of selling in bulk at a lower markup. Since their expenses are lower, wholesalers can still make a profit with lower prices.
If you sell both retail and wholesale, knowing how to differentiate your wholesale price from your recommended retail price is critical because your wholesale buyers are unlikely to accept your retail pricing model.
To ensure a healthy return on investment (ROI), the general rule of thumb is that your final selling price should be 50% of the retail price. A good pricing strategy, on the other hand, is highly dependent on your business, so there is no one-size-fits-all solution.
Competitive wholesale pricing is meant to boost your sales but getting the numbers wrong can cause big headaches for most distributors. Maintaining strong retailer relationships is crucial, as trust and long-term partnerships with retailers can significantly influence your pricing decisions and overall business success.
Read this FREE ebook Avoid the Top 5 Mistakes Wholesales Distributors Make and learn how to avoid pricing mistakes and other challenges faced by distributors.
Wholesale Price
Wholesale price refers to the price at which goods or services are sold in bulk to retailers, distributors, or other businesses, rather than directly to consumers. It’s typically lower than the retail price, as the buyer purchases a larger quantity and often assumes additional responsibilities like transportation and storage.

Avoid the Top 5 Mistakes Wholesale Distributors Make
Are you making one of the top 5 mistakes that plague wholesale distributors? Download our free eBook to find out. We’ve also included tips and guidance to help you save time and avoid costly mistakes.
Wholesale Price: A Closer Look
Wholesale prices can vary significantly depending on factors such as:
- Product type: Perishable goods like fresh produce may have more fluctuating wholesale prices due to factors like supply and demand.
- Market conditions: Economic fluctuations, competition, and global events can all impact wholesale prices.
- Geographic location: Transportation costs and regional market dynamics can influence pricing.
- Quantity purchased: Larger quantities often result in lower wholesale prices.
Wholesale Items Cheap
Wholesale items are products sold in bulk quantities directly to retailers or other businesses, rather than to individual consumers. This business model often offers significantly lower prices per unit compared to retail purchases. This reduction in cost is due to several factors:
- Economies of Scale: Wholesalers purchase large quantities of products directly from manufacturers, allowing them to negotiate lower prices.
- Reduced Overhead: Wholesalers typically have lower operating costs than retailers, as they don’t need to invest in extensive store setups or marketing campaigns.
- Simplified Sales Process: Wholesale transactions often involve fewer steps and less customer service overhead, further reducing costs.
Wholesale Business
A wholesale business involves buying goods in large quantities from manufacturers or distributors and selling them in smaller quantities to retailers or other businesses. Wholesalers act as intermediaries in the supply chain, facilitating the distribution of products from producers to end consumers. Successful wholesale businesses rely on efficient logistics, strong supplier relationships, and effective inventory management. They provide retailers with the products they need at competitive prices, enabling a smooth flow of goods through the market and contributing to overall economic efficiency.
A company can succeed in distribution channels by developing effective distributor and pricing strategies, building long-term relationships, and leveraging technology to enhance market positioning.
Wholesale Price Optimization for Retailers
Wholesale price optimization for retailers refers to the process of determining the ideal price to charge for products sold to retailers, wholesalers, or distributors. The goal of wholesale price optimization is to find a pricing strategy that maximizes revenue while remaining competitive in the market. Distributor pricing focuses on developing and refining pricing strategies within the distribution channel, taking into account supply chain efficiency and profit margins.
Retailers need to consider several factors when setting wholesale prices, such as the cost of production, distribution, and marketing, as well as the demand for the product, the competitive landscape, and the target market. A retailer must also factor in the profit margin required to ensure a viable business.
To optimize wholesale prices, retailers can use pricing analytics tools that use data and algorithms to identify pricing patterns and trends. These tools can help retailers analyze factors like seasonality, competitive pricing, and customer demand, to set optimal wholesale prices that maximize profitability and revenue.
Retailers can also use dynamic pricing strategies, which adjust wholesale prices in real-time based on market conditions, demand, and competition. This approach allows retailers to be more flexible in their pricing and take advantage of changing market conditions to increase profits.
Overall, wholesale price optimization is a critical component of a successful retail business. By finding the optimal pricing strategy, retailers can maximize revenue, increase profits, and stay competitive in their market.
How to Compute Reseller Price
To compute the reseller price, follow these steps:
Determine Wholesale Price: Start with the wholesale price of the product.
Add Markup: Apply the markup percentage you wish to achieve as a profit. This markup should cover operational costs, desired profit, and market conditions.
For instance, if the wholesale price is $20 and you want a 50% markup, the reseller price would be $30 ($20 + $10). This ensures that the reseller can cover costs and achieve a reasonable profit margin.
Typical Wholesale Markup
A typical wholesale markup is the percentage added to the wholesale cost to determine the retail price. The exact markup varies depending on factors such as industry standards, competition, product type, and desired profit margin. Common markup percentages range from 50% to 100%, but can be higher or lower depending on the circumstances.
Wholesale Fashion Pricing Strategy
Wholesale fashion pricing strategy involves setting prices for clothing and accessories sold in bulk to retailers. Key factors to consider include:
- Brand Positioning: High-end brands may charge premium wholesale prices, while more affordable brands may opt for lower prices.
- Product Quality and Material Costs: The quality of materials and manufacturing processes can impact pricing.
- Seasonal Trends and Demand: Prices can fluctuate based on current fashion trends and seasonal demand.
- Competitive Landscape: Monitoring competitors’ pricing can help inform strategic decisions.
3 Effective Steps to Set Wholesale pricing and How is Wholesale Pricing Calculated

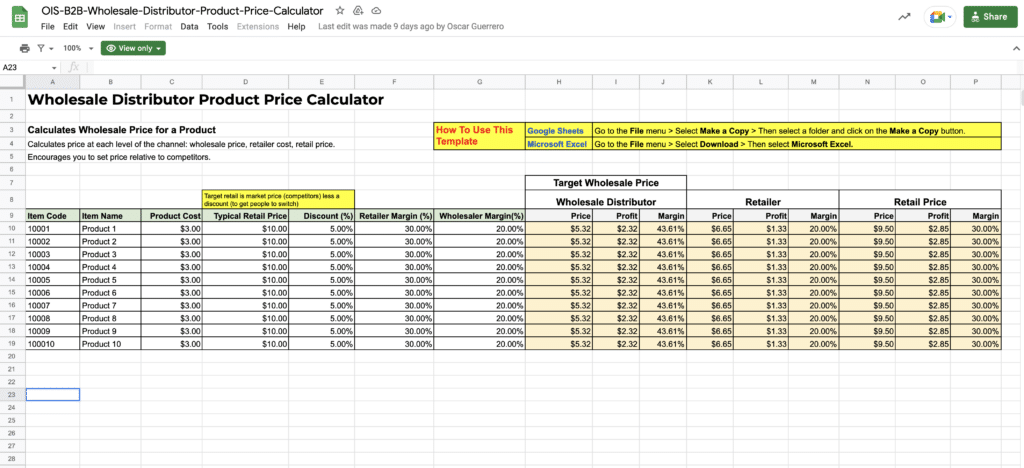
FREE Wholesale Pricing Calculator
Download your free wholesale pricing calculator now to get started.
1. Do market research
Determine your market segment and where you fit in before you set any product prices. For example, are you a discount brand, a contemporary brand, or a designer brand? This also influences how your target audience perceives you, which in turn influences your pricing.
If your competitive advantage is a lower price point, keep that in mind as you conduct your research. Be aware of your break-even point and use the break-even point formula to determine it.
Consider these factors when conducting market research if your target customers are more budget-conscious or looking for a high-quality, high-end product.
2. Calculate your cost of goods manufactured (COGM)
The basic price-setting formula is that products should sell for more than they cost you. Once you’ve determined how much your competitors are charging for comparable products, you can compare those figures to your production costs.
The COGM of a product can be calculated using the following formula:
Total Material Cost + Total Labor Cost + Additional Costs and Overhead = Cost of Goods Manufactured
Unless you are directly involved in manufacturing, you will have to purchase products from the people who make them. They have their own prices, and for each order, you must also consider:
- Shipping fees
- Administrative and processing costs for receiving products
- Failure or defective product rates
When you know how much a product costs, you can start thinking about profit margins. They should ideally be comparable to what your competitors are charging, At least, if you’re selling comparable-quality goods.
If you want to attract more customers, you can choose to offer lower prices than your competitors.
However, this means you’ll have lower profit margins. Higher prices, on the other hand, may not be well received by customers unless you are selling unique products or your quality is significantly higher.
3. Analyze retail prices
Prices for wholesale goods do not exist in a vacuum. If you have any doubts about your prices, you can refer to the three datasets listed below:
- Each product's basic production costs
- How much your wholesale competitors charge
- How much retail stores charge for the same items
Unless you’re missing something, there should be a difference between the two price lists.
When establishing wholesale pricing, it’s generally advisable to maintain parity with your competitors. Opting for significantly higher prices could encroach upon the profit margins of retailers, potentially diminishing your attractiveness as a supplier.
To make informed pricing decisions and effectively target your wholesale efforts, having access to a comprehensive list of retail stores within your desired market can provide valuable insights into the competitive landscape and potential customer base. This allows you to understand the existing retail environment and tailor your pricing strategy accordingly.
It’s useful to compare wholesale and retail figures in a spreadsheet for future reference. You’ll be able to appreciate the difference in margins between the two types of businesses for your specific niche this way.
If you’re interested in a wholesale to retail price calculator, Orders in Seconds offers a FREE Wholesale Price Calculator to help you figure out wholesale prices.
Wholesale Cost Definition
Wholesale cost refers to the price a retailer or distributor pays for a product directly from the manufacturer or supplier. It’s the base price upon which the retailer will calculate their profit margin and selling price. Wholesale costs typically exclude shipping, handling, and any additional fees.
CPG Wholesale Pricing
CPG (Consumer Packaged Goods) wholesale pricing refers to the pricing strategy used by manufacturers of consumer goods to sell their products to retailers or wholesalers. The pricing strategy aims to achieve the manufacturer’s financial goals while competitive prices to retailers.
Manufacturers must consider various factors when setting CPG wholesale prices, such as the cost of production, shipping, and distribution, marketing and advertising expenses, and the desired profit margin. They also need to consider the competitive landscape and demand for the product in the market.
Manufacturers typically offer volume-based discounts to retailers or wholesalers, with higher discounts offered for larger orders. This encourages retailers to purchase more products at once, increasing the manufacturer’s revenue while providing retailers with a competitive price.
Manufacturers may also offer promotional pricing to retailers or wholesalers, such as temporary discounts or rebates, to encourages retailers to promote their products to consumers. This can help increase sales and drive demand for the product.
In addition to volume-based discounts and promotional pricing, manufacturers may also use other pricing strategies, such as dynamic pricing, where prices adjust based on market conditions, and value-based pricing, where prices are based on the perceived value of the product.
Overall, CPG wholesale pricing is a critical aspect of a manufacturer’s business strategy. Developing an effective distributor pricing strategy is essential for ensuring consistency, profitability, and competitiveness across the supply chain. By setting the right prices, manufacturers can increase revenue, stay competitive, and built relationships with retailers and wholesalers.
Wholesale Rate
The wholesale rate is the price per unit at which goods are sold to retailers or resellers in bulk quantities. This rate is typically much lower than the retail price, allowing retailers to purchase large volumes of goods at a discounted rate. The wholesale rate is determined by various factors, including production costs, supply and demand dynamics, and the competitive landscape. Understanding the wholesale rate is crucial for retailers as it directly impacts their pricing strategies and profit margins.
2 Types of Formulas to Calculate Wholesale Price
There are numerous wholesale pricing strategies available, but don’t worry—learning them all isn’t necessary if you’re new to selling wholesale. Instead, let’s go over two quick and easy wholesale pricing methods you can use right now.
Absorption Pricing Formula
There are numerous wholesale pricing strategies available, but don’t worry—learning them all isn’t necessary if you’re new to selling wholesale. Instead, let’s go over two quick and easy wholesale pricing methods you can use right now.
The formula for absorption pricing is as follows:
Wholesale Price = Cost Price + Profit Margin
Are you unsure how to calculate the cost price?
You’ll need to understand your costs of goods sold (COGS) as well as your overhead costs. Here’s a quick refresher:
- Calculate your cost of goods sold.
- Calculate your overhead costs.
- Total the two expenses.
- Once you have those two numbers, add them together to get your formula's total cost price.
Absorption pricing method pros:
- It is simple to use and does not necessitate any training or complicated formulas.
- Your profits are almost certain. If you can account for all expenses, you should be able to turn a good profit.
Absorption pricing method cons:
- Pricing gaps are common, and no competitor pricing is taken into account.
- This method does not take into account value perception. You might charge too much, sending potential customers elsewhere.
Wholesale vs. Retail Price Formula
The wholesale vs. retail price formula is a simple calculation to determine the retail price based on the wholesale cost and desired markup percentage. The formula is:
- Retail Price = Wholesale Cost * (1 + Markup Percentage)
For example, if the wholesale cost is $50 and the desired markup is 50%, the retail price would be $50 * (1 + 0.5) = $75.
Differentiated Pricing Formula
Differentiated pricing is a wholesale pricing method that calculates demand for a product to optimize return on investment (ROI). Different buyers in different situations pay different prices for the same product in this case.
This pricing method, also known as demand pricing or time-based pricing, is based on the idea that buyer acceptance determines the price in any given market condition.
For example, if you sell swimsuits, you can charge more than the average market price during peak seasons. You’ll notice that the price of swimsuits in retail stores can quickly rise at the start of the summer season, then drop after demand drops.
This also applies to areas where there is less competition and customers typically pay a higher price for products, such as a beach resort or an airport.
Wholesalers can also offer products at a lower price by using differentiated pricing. For example, if you have too much old stock on hand, you can run a last-minute flash sale and still make a profit.
Differentiated pricing method pros:
- This method can provide the best return on investment. It allows you to take advantage of market scenarios in real-time, stay competitive, and gather buyer data.
- When a product is in high demand, buyers are often willing to pay a premium, which means more profit for you. Differentiated pricing can be used to sell trending products and other items that are hard to find or extremely popular.
Differentiated pricing method cons:
- There is a fine line between profit maximization and overcharging wholesale customers. If you are perceived as opportunistic, or if people believe you are price-gouging them, your brand's reputation will suffer.
Wholesale Prices Meaning
Wholesale prices refer to the cost charged by manufacturers or distributors to retailers or resellers when they purchase goods in large quantities. These prices are typically lower than retail prices because wholesalers sell in bulk, and the cost per unit decreases with volume. Wholesale pricing allows retailers to purchase products at a reduced cost, which they can then mark up when selling to consumers, thereby making a profit. This pricing strategy is essential for the supply chain, enabling a wide distribution of products and ensuring that retailers can offer competitive prices to end consumers.
What Does Wholesale Price Mean?
The term “wholesale price” signifies the amount charged by a producer or distributor when selling goods in large quantities to a retailer or reseller. This price is generally lower than the retail price, reflecting the economies of scale achieved through bulk purchasing. Wholesale pricing is designed to enable retailers to buy products at a lower cost, which they can then sell at a higher price, thereby generating a profit margin. It is a fundamental aspect of the supply chain, ensuring that products move efficiently from production to consumption.
Standard Wholesale Discount
The standard wholesale discount is a percentage reduction off the retail price that manufacturers or distributors offer to retailers who purchase goods in bulk. This discount varies by industry and product but typically ranges from 30% to 50%. For example, if a product’s retail price is $100 and the standard wholesale discount is 40%, the wholesale price would be $60. Offering such discounts incentivizes retailers to buy in larger quantities, ensuring higher sales volumes for the manufacturer.
Using Technology to Streamline Pricing
Leveraging technology is essential for distributors aiming to optimize their pricing strategies and boost profit margins. Advanced pricing software and data analytics tools enable distributors to automate complex pricing models, reducing manual errors and saving valuable time. For example, configure price quote (CPQ) solutions can streamline the process of generating accurate quotes, even when dealing with intricate pricing structures. By analyzing real-time data on customer demand, market trends, and competitor pricing, distributors can make informed pricing decisions that align with current market conditions. Embracing technology not only enhances pricing efficiency but also empowers distributors to respond quickly to shifts in demand, ultimately supporting more profitable and customer-focused pricing strategies.
Implementing a Pricing Strategy
Successfully implementing a pricing strategy involves a thorough understanding of production costs, market dynamics, and customer demand. Distributors must conduct detailed market research to identify their target market and target customers, ensuring that their pricing models reflect both business objectives and market realities. Whether using value based pricing, cost-plus, or dynamic pricing, a good pricing strategy should be flexible enough to adapt to changing market conditions and customer preferences. By continuously evaluating production costs and competitor pricing, distributors can set prices that maximize profitability while remaining attractive to customers. Ongoing assessment and adjustment are key to ensuring that the chosen pricing strategy continues to deliver results as the market evolves.
Monitoring and Adjusting Prices
Continuous monitoring and adjustment of prices are crucial for maintaining a competitive pricing strategy in today’s dynamic market. Distributors should regularly analyze sales data, customer demand, and market trends to identify when pricing changes are necessary. Utilizing pricing analytics tools and conducting ongoing market research allows distributors to make data-driven decisions, ensuring their prices remain aligned with both customer expectations and competitive pressures. Implementing clear pricing policies, such as price matching or guarantees, can further reinforce a commitment to competitive pricing and foster customer trust. By staying proactive and responsive, distributors can adapt their pricing to market shifts, optimize sales, and strengthen their market position.
Distributor Price vs. Wholesale Price
While the terms distributor price and wholesale price are often used interchangeably, there are key differences between them. The wholesale price is the cost at which a product is sold to retailers or resellers who then sell it to end consumers. On the other hand, the distributor price is the cost at which a distributor purchases goods from a manufacturer before selling them to wholesalers or directly to retailers. Distributors often handle logistics, storage, and transportation, which can add to the cost. As a result, the distributor price might include additional fees compared to the wholesale price, reflecting the value-added services provided by distributors.
Wholesale vs. Retail Price
The wholesale price is the amount charged by manufacturers or wholesalers to retailers, who then sell the products at the retail price to consumers. The retail price is typically significantly higher than the wholesale price, as it includes not only the cost of the product but also a markup to cover operating expenses and generate profit for the retailer. This markup accounts for costs such as rent, salaries, utilities, and marketing. The difference between wholesale and retail prices allows retailers to sustain their business operations while providing consumers with the goods they desire.
What Does MSRP Mean in Wholesale
MSRP, or Manufacturer’s Suggested Retail Price, is a recommended selling price set by the manufacturer. It serves as a guideline for retailers when pricing their products. In the context of wholesale, the MSRP helps wholesalers and distributors understand the market value of a product and establish a pricing strategy that ensures competitiveness while allowing retailers to achieve a reasonable profit margin. While the MSRP is not mandatory, adhering to it can help maintain price consistency across different sales channels, enhancing brand perception and customer trust.
Wholesale Pricing Strategy
A successful wholesale pricing strategy involves setting prices that attract retailers while ensuring profitability for the wholesaler. This strategy typically includes a thorough analysis of production costs, market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product. Wholesalers may offer tiered pricing based on order volume, with discounts for larger purchases to incentivize bulk buying. Additionally, maintaining a balance between competitive pricing and profitability is crucial. Strategic considerations may also include seasonal pricing adjustments, promotional offers, and loyalty programs to build long-term relationships with retailers and encourage repeat business.
Solutions to Protect Wholesale Profit Margins
Wholesale businesses face various challenges in maintaining profitability. Here are some strategies to protect and improve wholesale profit margins:
- Negotiate better deals: Work closely with suppliers to secure favorable terms, including discounts for bulk purchases or timely payments.
- Optimize inventory management: Avoid overstocking or understocking to minimize holding costs and prevent markdowns.
- Enhance operational efficiency: Streamline processes, reduce waste, and invest in technology to improve productivity.
- Diversify product offerings: Offer a wider range of products to attract more customers and reduce reliance on any single item.
- Explore new markets: Expand into new geographic regions or customer segments to increase sales.
- Implement pricing strategies: Consider strategies like dynamic pricing or tiered pricing to adjust prices based on market conditions or customer behavior.
Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit margin is a key financial metric that represents the percentage of revenue that exceeds the cost of goods sold (COGS). It is calculated by subtracting COGS from total revenue and then dividing the result by total revenue. For wholesalers, the gross profit margin indicates the efficiency of production and the effectiveness of pricing strategies. A higher margin suggests that the business is able to cover its production costs and still make a substantial profit. Monitoring gross profit margin helps wholesalers make informed decisions about pricing, cost control, and overall financial health.
Bulk Pricing
Bulk pricing refers to the strategy of offering lower prices per unit to customers who purchase large quantities of a product. This pricing model benefits both wholesalers and retailers by encouraging larger orders, reducing inventory turnover time, and achieving economies of scale. For wholesalers, bulk pricing helps move large volumes of stock quickly, ensuring steady cash flow and reducing storage costs. Retailers, in turn, benefit from lower per-unit costs, allowing them to improve their profit margins or pass savings on to consumers, making their offerings more competitive. Bulk pricing is a vital component of wholesale operations, driving sales and fostering strong business relationships.
Wholesale Examples
Wholesale transactions occur in various industries. Here are some common examples:
- Grocery stores: Purchase large quantities of food products from distributors.
- Retailers: Buy clothing, electronics, and other goods from manufacturers or wholesalers.
- Restaurants: Obtain ingredients and supplies from foodservice distributors.
- Industrial manufacturers: Procure raw materials and components from suppliers.
- Online marketplaces: Facilitate wholesale transactions between sellers and buyers.
By understanding the dynamics of wholesale pricing and implementing effective strategies, businesses can protect their profit margins and achieve long-term success.
Conclusion
Setting prices for your store is never easy. Wholesale prices should be lower than retail prices on average.
However, before you set a price, you must ensure that all costs have been considered. That means taking into account production, administrative, and handling costs before even considering a wholesale margin profit.
If you use Orders in Seconds for your B2B wholesale distribution business, you can offer wholesale pricing at the group, category, and brand levels, chain store or single store level, or special prices on discounted products.
If you would like to learn more about a wholesale software solution to automate product pricing for field sales reps or B2B eCommerce, please contact Orders in Seconds.
Quoting for Distributors
When quoting for distributors, it’s crucial to strike a balance between profitability and competitiveness. Factors to consider include the distributor’s order volume, their target market, and their existing relationships with other suppliers. Offering tiered pricing based on order size can incentivize larger orders. Additionally, transparent and clear communication regarding pricing, delivery terms, and any potential discounts can build trust and long-term relationships with distributors.
Define Wholesale Price
The wholesale price is the price at which a manufacturer or distributor sells goods in bulk to retailers. It’s typically lower than the retail price, allowing retailers to mark up the products and make a profit. Wholesale prices can vary based on factors such as order volume, product demand, and market competition.
Pricing Techniques Used by Retailers
Retailers employ a variety of pricing techniques to attract customers and maximize profits.
- Cost-plus pricing: This method involves adding a markup percentage to the cost of goods sold.
- Value-based pricing: This method focuses on the perceived value of the product to the customer and sets prices accordingly.
- Competitive pricing: This method involves setting prices based on the prices of competitors.
- Psychological pricing: This method uses techniques such as odd-even pricing ($9.99 instead of $10) to create a perception of value.
Bulk Costing
Bulk costing refers to the practice of offering lower prices for larger quantities of goods. This strategy encourages larger orders and can be beneficial for both the seller and the buyer. For the seller, it can increase revenue and improve cash flow. For the buyer, it can reduce per-unit costs and improve profitability.
Consumer Packaging Goods Pricing Strategy
Pricing consumer packaged goods (CPGs) requires careful consideration of various factors.
- Target market: Understanding the demographics and preferences of the target audience is crucial.
- Brand positioning: Pricing should align with the brand’s image and positioning in the market (e.g., premium, budget).
- Competition: Analyzing competitor pricing is essential to remain competitive.
- Product life cycle: Pricing strategies may need to be adjusted throughout the product life cycle (introduction, growth, maturity, decline).
Efficient Inventory Management
Efficient inventory management is critical for businesses of all sizes. It involves accurately tracking inventory levels, minimizing stockouts and overstocking, and optimizing the flow of goods. Techniques such as just-in-time (JIT) inventory, first-in, first-out (FIFO) inventory valuation, and the use of inventory management software can help businesses improve efficiency and reduce costs.
Product ID
A product ID is a unique identifier assigned to a specific product. It can be a number, a code, or a combination of characters. Product IDs are used to track inventory, manage orders, and generate reports. Common types of product IDs include stock keeping units (SKUs), universal product codes (UPCs), and international standard book numbers (ISBNs).
Data Structure
A data structure is a way of organizing and storing data in a computer so that it can be accessed and used efficiently. Common data structures include arrays, linked 1 lists, trees, graphs, and hash tables. The choice of data structure depends on the specific needs of the application.
Key Value Pairs
Key-value pairs are a fundamental data structure where each piece of data is associated with a unique identifier (key). This allows for efficient data retrieval and manipulation. Key-value pairs are used in various applications, including databases, configuration files, and caching systems.
Managing Inventory
Managing inventory involves a range of activities, including:
- Forecasting demand: Predicting future sales to ensure adequate stock levels.
- Ordering and receiving goods: Efficiently placing orders with suppliers and receiving goods.
- Storing and handling inventory: Properly storing and handling inventory to prevent damage and spoilage.
- Tracking inventory levels: Maintaining accurate records of inventory levels using inventory management systems.
- Analyzing inventory performance: Regularly analyzing inventory data to identify areas for improvement.