Have you ever wondered about the importance of a well-designed warehouse layout? An efficient warehouse layout design can make all the difference in improving productivity, safety, and customer satisfaction. In this article, we will explore the complexity of warehouse layout design, its significance, key components, and best practices.
Key Takeaways
- Optimizing warehouse layout design is essential for efficient operations, increased storage capacity and product flow, as well as customer satisfaction.
- When designing a warehouse layout various factors such as type of operation, products stored, equipment, and space must be taken into account to maximize efficiency.
- Tools such as Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) can aid in optimizing the warehouse layout by providing features like automated pick lists and labor planning.
Table of Contents
- The Importance of Warehouse Layout Design
- Key Components of an Efficient Warehouse Layout
- Warehouse Layout Design Considerations
- Steps for Planning an Optimal Warehouse Layout
- Warehouse Layout Design Types: U-shaped, I-shaped, and L-shaped
- Technologies and Tools for Warehouse Layout Design
- Warehouse Layout Design Best Practices
- Overcoming Common Warehouse Layout Challenges
- The Role of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) in Layout Design
- Summary
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Elevate Your Business with Orders in Seconds
The Importance of Warehouse Layout Design

Optimization of operations through an efficient warehouse layout has a significant impact on a company’s profitability and customer satisfaction. So, how do we achieve this? Implementing a combination of warehouse picking strategies such as the following are key
- Zone Picking
- Batch Picking
- Wave picking
- Discrete picking
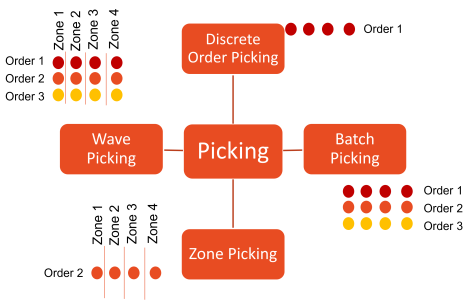
These combined warehouse picking strategies allow warehouse managers to streamline the order fulfillment process, ensuring that warehouse staff can efficiently navigate the warehouse floor and locate items with ease. Adopting a well-planned warehouse layout design allows businesses to enhance their storage capacity and fully utilize the available warehouse space, ultimately leading to improved inventory visibility and a better understanding of stock levels.
It’s worth noting that not knowing what’s in stock is one of the biggest mistakes for wholesale distributors. To learn more about this critical issue and discover other common mistakes you might be making, we invite you to explore our free eBook Avoid the 5 Mistakes Wholesale Distributors Make.

Avoid the Top 5 Mistakes Wholesale Distributors Make
Finally, an effective warehouse layout starts with a thoughtful warehouse diagram that considers space optimization and the needs of warehouse workers. A well-designed layout maximizes vertical storage and ensures a seamless product flow from storage to shipping, thereby reducing the time required to fulfill multiple orders.
Key Components of an Efficient Warehouse Layout

The essential elements of an effective warehouse layout include:
- Receiving area
- Storage area
- Picking area
- Packing area
- Shipping area
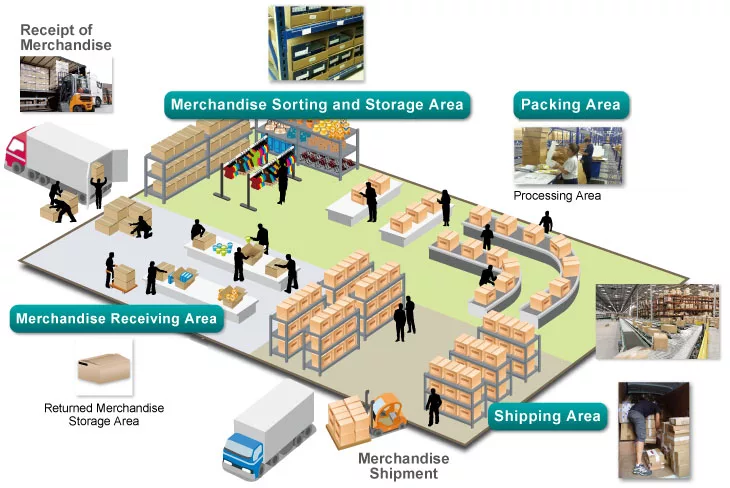
Each of these areas contributes to a seamless order fulfillment process, from the receipt of goods at the warehouse to their dispatch to customers.
The picking strategy, a crucial aspect of an efficient warehouse layout, is employed to enhance the warehouse picking process. Some popular picking strategies include:
- Batch picking
- Wave picking
- Zone picking
- Discrete picking
Selecting the right picking strategy can lead to more efficient routes and reduced operating costs, ultimately contributing to a more efficient warehouse layout.
Besides the picking process, storage areas also have a significant role in warehouse space utilization. Some commonly employed storage and shelving equipment in warehouses include:
- Pallet racks
- Heavy- and light-duty shelving
- Cantilever racks
- Bins
Furthermore, the utilization of efficient equipment options, such as autonomous mobile robots and pallet jacks, can significantly contribute to the overall efficiency of the warehouse layout.
Warehouse Layout Design Considerations

Several factors need to be considered when designing a warehouse layout. These include:
- The type of operation
- The products being stored
- The necessary equipment
- The available space
- The workflow implementation
- Safety regulations
- Cost efficiency
By considering these aspects, warehouse managers can design a layout that meets the unique requirements of their operations while maximizing efficiency and safety.
For instance, the type of operation and the nature of the products being stored will dictate the kind of storage needed in the warehouse layout. Considering these factors enables warehouse managers to maximize space utilization, maintain inventory accuracy, and enhance the overall efficiency of the warehouse.

Planning an optimal warehouse layout involves the following steps:
Analyzing current operations
Identifying opportunities for improvement
Selecting the appropriate design type
Testing and refining the layout for maximum efficiency
Each of these steps will be explored in more detail in the following subsections.
Analyzing Current Operations
The first step in optimizing a warehouse layout is to analyze the existing warehouse layout, processes, and equipment. This involves evaluating the current configuration of the warehouse, including its size and shape, the number of aisles, the type of storage systems, and the location of loading docks. By assessing the existing layout, warehouse managers can gain insights into the areas that require improvement.
Besides the layout, evaluating the current processes and equipment used in the warehouse, like the type of forklifts, inventory management systems, and order fulfillment systems, is also important. Identifying areas for improvement in these aspects of the warehouse operations can lead to significant enhancements in efficiency and productivity.
After analyzing the current operations, the subsequent step is to pinpoint opportunities for improvement. This may include reorganizing the warehouse to minimize the distance between departments, optimizing the flow of goods, and augmenting the storage capacity.
Additionally, modifications can be made to the equipment and processes to enhance efficiency and productivity. Some ways to achieve this include:
- Implementing automated systems, such as conveyor belts and robots, to reduce manual labor and increase accuracy
- Streamlining the order fulfillment process
- Executing a just-in-time inventory system
- Incorporating new technologies, such as RFID tags, to improve warehouse efficiency
These strategies can help optimize operations and improve overall productivity in the warehouse.
Selecting an appropriate design type for warehouse layout planning requires considering factors like:
- The size of the facility
- Warehouse equipment
- Legal requirements
- The specific needs of your operations
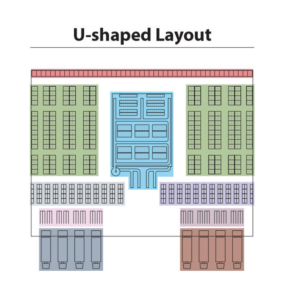
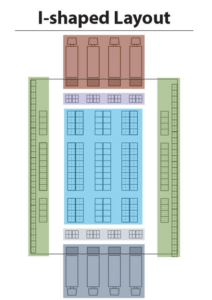
The most common design types for warehouse layout planning are U-shaped, I-shaped, and L-shaped layouts, each designed to optimize order picking and other warehouse operations.
The U-shaped design is suitable for operations with a substantial number of SKUs and a considerable volume of orders, while the I-shaped design is more appropriate for operations with fewer SKUs and lower order volumes.
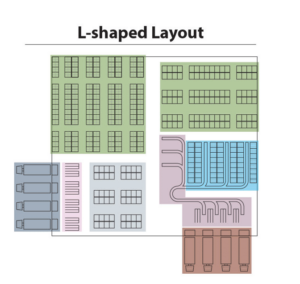
The L-shaped design is optimal for operations with a large number of SKUs and a high volume of orders, but with limited space, making ample space a crucial factor to consider.
Once the suitable design type is chosen, the layout should be tested and refined. This involves simulating the proposed design, identifying potential issues, and making adjustments as needed to optimize efficiency and safety. Refining the layout allows warehouse managers to ensure smooth and efficient warehouse operations.
Assessing time and cost savings, as well as the overall efficiency and productivity of the warehouse, helps evaluate the effectiveness of the modifications. This will help warehouse managers determine whether the changes made to the warehouse layout have had a positive impact on the overall efficiency of the warehouse operations.
Warehouse Layout Design Types: U-shaped, I-shaped, and L-shaped

Each design type for warehouse layout possesses unique advantages and is suitable for different operations and available space.
The U-shaped design consists of a semi-circular design with loading and shipping areas adjacent, a reception area situated behind the loading and picking area, and a storage area completing the back of the warehouse. This design type is particularly suitable for operations with a substantial number of SKUs and a considerable volume of orders, especially when efficient loading and unloading areas are crucial.
The I-shaped design, on the other hand, is more appropriate for operations with fewer SKUs and lower order volumes. This design type features a linear layout, with the storage, loading, and shipping areas arranged in a straight line, optimizing the flow of goods throughout the warehouse.
Lastly, the L-shaped design is optimal for operations with a large number of SKUs and a high volume of orders, but with limited space. In this design type, the traffic flow is arranged in an “L” configuration, with loading and reception areas situated on one side and shipping and picking areas located on the opposing side. By understanding the unique characteristics of each design type, warehouse managers can select the most suitable layout for their specific needs.
Technologies and Tools for Warehouse Layout Design

In the modern digital age, a range of technologies and tools exists to aid in warehouse layout design. Some of these tools include:
- Specialized software, such as Icograms Designer, SmartDraw, and Computer-Aided Design (CAD) tools
- These tools can be employed to create detailed and accurate warehouse diagrams
- Warehouse managers can use these tools to visualize their layout and make necessary adjustments before implementation.
In addition to software, automation systems and warehouse management systems (WMS) can be utilized to optimize the layout and enhance overall efficiency. By using these technologies and tools, warehouse managers can streamline their operations, improve inventory management, and ultimately increase the efficiency of their warehouse layout design.
Warehouse Layout Design Best Practices

Key best practices for warehouse layout design include:
- Maximizing space utilization
- Enhancing accessibility
- Planning for change
- Incorporating technology
- Prioritizing safety
By adhering to these best practices, warehouse managers can create an efficient warehouse layout that meets their specific needs and optimizes their operations.
Maximizing storage space utilization can be achieved through the use of vertical storage, multi-level shelving, and automated storage and retrieval systems. Improving accessibility involves ensuring that the warehouse is easy to navigate, with clear pathways and aisles, and a layout designed to reduce the need for employees to travel long distances.
Planning for change in a warehouse layout implies designing a flexible and adaptable layout that can accommodate changing needs. Some strategies for achieving this include:
- Using easily reconfigurable modular shelving and storage systems
- Integrating technology into the warehouse layout, such as automated systems for inventory tracking and order fulfillment
- Implementing robotics and automation for material handling
By incorporating these strategies, you can create a warehouse layout that is able to adapt to future changes and improve overall efficiency.
Safety prioritization encompasses providing adequate lighting, incorporating safety signage, and guaranteeing an ergonomically designed layout.
Overcoming Common Warehouse Layout Challenges

Optimizing space utilization, accounting for structural constraints, integrating automation, and ensuring compliance with safety regulations are common warehouse layout challenges. Warehouse managers can utilize diverse strategies to overcome these challenges.
Optimizing the layout of the warehouse, utilizing vertical space, and using efficient storage solutions are effective strategies for maximizing warehouse space and ensuring sufficient space. When considering structural limitations, warehouse managers should take into account the size and shape of the warehouse, the weight of the items to be stored, and the height of the ceilings.
Integrating automation into the warehouse layout can be achieved through the use of automated storage and retrieval systems, automated conveyor systems, and automated sorting systems. Lastly, adhering to fire safety regulations, hazardous material regulations, and ergonomic requirements is essential for ensuring compliance with safety requirements.
The Role of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) in Layout Design

Warehouse management systems (WMS) aid in warehouse layout design by identifying inefficient use of space, recommending improved layouts, and optimizing storage locations and productive routes. By utilizing a warehouse management system, warehouse managers can design and manage their warehouse layout accurately, ensuring the optimization of space utilization and enhancing operational efficacy.
The advantages of using a WMS for warehouse layout design go beyond the layout itself. WMS can enhance efficiency while maintaining order fulfillment accuracy by:
- Generating pick lists automatically
- Displaying product availability precisely
- Offering real-time insight into order status
- Assisting in forecasting when to replenish inventory through reorder point notifications
- Aiding in planning staff labor
Warehouse managers can optimize their warehouse layout and enhance overall efficiency by harnessing the capabilities of WMS.
Summary
In conclusion, an efficient warehouse layout design is vital for optimizing operations, safety, and productivity, ultimately impacting a company’s profitability and customer satisfaction. By understanding the importance of warehouse layout design, incorporating key components, following best practices, and utilizing the latest technologies and tools, warehouse managers can create a warehouse layout that caters to their specific needs and optimizes their operations. As the world of warehousing continues to evolve, staying ahead of the curve and embracing innovative warehouse layout design strategies will undoubtedly be crucial to success.
Frequently Asked Questions
The most common warehouse layout is U-shaped, featuring receiving docks, unloading area, dynamic and static shelving, packing area, and shipping staging area. This allows for efficient workflows from beginning to end.
What are the 4 types of warehouse layouts?
When considering a warehouse layout design, four common arrangements optimize pickup travel time: U-shaped, L-shaped, I-shaped, and fishbone.
What are the 5 areas of a warehouse?
The 5 areas of a warehouse are docks and loading/unloading, receiving and staging, storage, picking, and shipping.
What is the best warehouse design layout?
For the best warehouse design layout, a U-shaped design is the most common and effective choice. This features receiving docks on one side, with dynamic and static shelving, unloading areas, and packing areas forming a U through the building.
How do you design a warehouse layout?
To design an effective warehouse layout, identify needs and current shortcomings, design for uninterrupted flow, allocate space for equipment and workstations, ensure that all products and pallets are accessible, and test the floor plan before implementation. Additionally, space out the loading and unloading area, separate the reception area, organize the storage area, create a separate picking area, and adjust the shipping and packing area.
Elevate Your Business with Orders in Seconds
While an effective warehouse layout is a crucial concern for distributors aiming to streamline their order fulfillment process, it’s essential to remember that efficiency begins at the very start.
OIS Pro App is designed to help your presales and DSD teams take orders seamlessly, saving valuable time and improving accuracy. If you’d like to learn more about how we can enhance your order fulfillment process, we invite you to schedule a demo today.





