In an era where the retail industry is having a hard time, it pays to look for ways to improve sales efficiency and cut costs. The latter needs to be done without impacting on customer satisfaction, and there can be no cutting corners when it comes to providing the best service. What are the answers? One of them is to look at Direct Store Delivery (DSD) and, where possible, perhaps implement it in your structure.
What is DSD, and why are more suppliers and retailers benefiting from this method of streamlining an operation? Let’s take a closer look at the Direct Store Delivery model, how it works and why it is becoming a popular sales channel to grow DSD sales.
The 21st century sales representative works in an entirely different world to that of even 20 years ago. Gone are the days when you went to visit a potential client, took the order and headed back to the main office, all in good time! Today, the key lies in responding to leads in double-quick time, getting the go ahead as soon as you can, and getting that order back to the team at the office almost in an instant – and quicker if possible! The world of commerce and industry is very much time-driven now, so any tool that can help the rep out in the field is always going to be welcome.
What is DSD?
Direct store delivery (DSD) is a supply chain management practice where the manufacturer delivers products directly to retail stores, bypassing traditional distribution centers.
Traditionally, a manufacturer produces items which – when ordered by the retailer – are then sent to the retailer’s distribution center. This can be a large warehouse in which goods are stored, waiting to be delivered to individual shops when required. This method has been used for many years by retailing chains, and it can be very efficient and successful.
Yet, in this day and age, is there really a need for that central distribution centre? The warehouse costs money to operate, after all. What if you could do away with that central distribution centre – and the costs it entails – and deliver direct from supplier to the individual store? That’s what DSD is about; it’s a method of distribution that avoids the added cost of the centralized distribution model.
About Direct-Store Delivery (DSD):
Direct-Store Delivery (DSD) is a distribution and supply chain strategy in which suppliers or manufacturers deliver their products directly to retail stores, bypassing traditional distribution centers or warehouses. This approach is commonly used for perishable goods, snacks, and other fast-moving consumer goods (FMCG) with a short shelf life.
While Direct-Store Delivery offers several advantages, it may also pose challenges such as increased transportation costs and complexities in managing a decentralized distribution system. The suitability of DSD depends on the nature of the products, the industry, and the specific requirements and preferences of the retailers involved.
DSD Models Types
These are the two types of Direct Store Delivery (DSD) models:
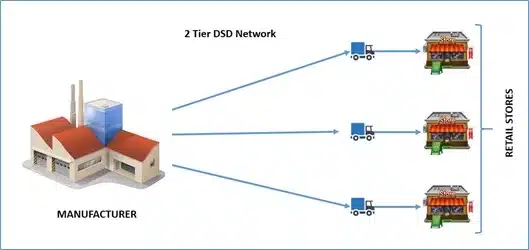
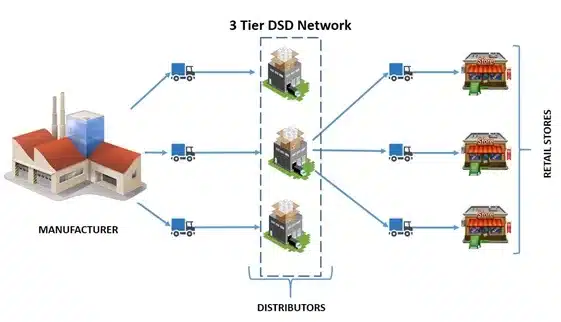
The Direct-Store Delivery Process
The Direct-Store Delivery (DSD) process involves several steps from the manufacturer or supplier to the retail store. The specific details can vary based on the industry, products, and companies involved, but here is a general overview of the DSD process:
- Order Placement: Retailers place orders for products directly with the manufacturer or supplier. This can be done through various communication channels, including electronic data interchange (EDI), online portals, or traditional methods.
- Order Fulfillment: The manufacturer or supplier processes the order and prepares the products for delivery. This may involve picking, packing, and labeling items based on the retailer’s requirements.
- Loading and Transportation: The products are loaded onto delivery vehicles, which are often trucks or vans. These vehicles transport the goods directly from the supplier’s distribution center to the retail store.
- Delivery to Store: Upon arrival at the store, the delivery personnel unload the products and deliver them directly to the store’s inventory or sales floor. This bypasses the need for the products to go through a central distribution center.
- Merchandising and Display: In some cases, the delivery personnel or representatives from the supplier may assist with merchandising the products on the shelves or displays within the store. This can include setting up promotional materials, ensuring proper product placement, and optimizing shelf space.
- Inventory Management: The store updates its inventory records to reflect the received products. This step is crucial for maintaining accurate stock levels and facilitating timely reordering.
- Payment and Invoicing: Invoicing and payment processes are typically handled directly between the supplier and the retailer based on agreed-upon terms. This can involve electronic invoicing systems and automated payment methods.
- Communication and Collaboration: Throughout the DSD process, there is ongoing communication and collaboration between the supplier and the retailer. This includes sharing information on product availability, promotions, and any other relevant updates.
- Monitoring and Analytics: Both the supplier and the retailer may monitor and analyze key performance indicators (KPIs) related to the DSD process. This can include sales data, inventory turnover, and other metrics to assess the effectiveness of the direct delivery strategy.
It’s important to note that the DSD process is designed to be agile and responsive to changes in demand and market conditions. The direct interaction between the supplier and the retailer allows for quick adjustments to optimize product availability and sales.
DSD Distribution: Efficient Delivery for Products and Services
One of the key advantages of DSD distribution is its ability to ensure timely and reliable delivery. By bypassing traditional distribution channels, DSD allows for direct control over the entire supply chain, from production to delivery. This results in faster turnaround times, reduced inventory holding costs, and improved product availability on store shelves. For businesses, this means increased sales opportunities and enhanced customer satisfaction.
In addition to speed and efficiency, DSD distribution offers a high level of flexibility and customization. Since the products are delivered directly, companies can tailor their deliveries to meet specific store requirements, such as product assortment, quantities, and promotional materials. This personalized approach helps businesses establish strong relationships with retailers and provides them with the opportunity to respond quickly to market demands and trends.
What does DSD mean in retail and what are the benefits of DSD for both supplier and retailer?
Retail DSD solutions refer to the process of delivering products directly from a manufacturer or distributor to retail stores, bypassing intermediaries such as warehouses or distribution centers. This type of distribution method is commonly used for perishable goods such as food and beverages, as well as for high-demand, fast-moving consumer goods.
For the retailer, not having to rely upon a central distribution center means quicker delivery time. Rather than loading, delivering to the warehouse, then loading again for delivery to the retail unit there is one simple transaction: load at the suppliers, deliver and unload at the retailer. This cuts out not only time, but money.
It also means the retail store has direct control at all times over inventory, and can handle stock control much more accurately. Unsurprisingly, DSD is most used in the food and drinks industry, where quick delivery and fast turnaround are part of the deal. Being able to order directly means getting things in store at the right time, ready for sale while still fresh.
With frequent deliveries and no need for large amounts of stock in holding, you also get the benefit of less waste and also reduced incidents of theft. Storage space can be utilized in other ways, too, and quality control becomes easier.
For the supplier, DSD allows for greater flexibility in production and logistics, along with the cost savings that come with both. It is now a proven method of getting goods from supplier to retailer, and one that you might want to take a closer look at. With online retailing rising in popularity, physical retailers need all the help they can find, and switching to DSD may be one of those opportunities.
Direct Store Delivery Best Practices
Implementing Direct Store Delivery (DSD) successfully involves following best practices to optimize efficiency, maintain product quality, and foster positive relationships between suppliers and retailers. Here are some key best practices for DSD:
- Communication and Collaboration: Maintain open and transparent communication between suppliers and retailers. Regularly share information on product availability, promotions, and any changes in the delivery schedule.
- Real-Time Data Sharing: Utilize technology for real-time data sharing. This includes using electronic data interchange (EDI), advanced shipment notifications, and other systems to provide accurate and up-to-date information on inventory levels, shipments, and sales.
- Route Optimization: Optimize delivery routes to minimize transportation costs and reduce delivery times. Use route planning software to ensure efficient and timely deliveries.
- Flexible Delivery Scheduling: Offer flexibility in delivery scheduling to accommodate variations in demand. This helps retailers manage their inventory more effectively and reduces the risk of stockouts or overstock situations.
- Inventory Visibility: Implement systems that provide both suppliers and retailers with real-time visibility into inventory levels. This enables better demand forecasting, reduces stockouts, and helps prevent overstock situations.
- Merchandising Support: Provide merchandising support to retailers, including assistance with product placement, promotional displays, and signage. This ensures that products are presented attractively and can lead to increased sales.
- Training and Education: Train delivery personnel and retail staff on the specifics of the DSD process, including handling procedures, merchandising guidelines, and any promotional activities. Well-trained staff contribute to smoother operations and enhanced customer satisfaction.
- Quality Control: Implement rigorous quality control measures to ensure that products delivered to stores meet the expected standards. This is crucial for maintaining customer satisfaction and brand reputation.
- Efficient Invoicing and Payment Processes: Streamline invoicing and payment processes to reduce administrative burdens. Consider using electronic invoicing and automated payment systems to improve efficiency and accuracy.
- Performance Metrics and Analysis: Establish key performance indicators (KPIs) and regularly analyze them to assess the effectiveness of the DSD process. This can include metrics related to on-time deliveries, order accuracy, inventory turnover, and sales performance.
- Adaptability to Market Changes: Stay agile and be ready to adapt to changes in market conditions, consumer preferences, and other external factors. A flexible DSD strategy allows for quick adjustments to optimize performance.
- Compliance with Regulations: Ensure compliance with relevant regulations, including transportation and safety standards. Adhering to legal requirements helps prevent disruptions in the supply chain and ensures the safety of products.
By incorporating these best practices, businesses can enhance the effectiveness of their Direct Store Delivery operations, leading to improved customer satisfaction, better inventory management, and stronger relationships between suppliers and retailers.
DSD Inventory: Managing Direct Store Delivery Products
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) is a retail distribution method where products are delivered directly from the manufacturer or distributor to the retail store, bypassing the warehouse or distribution center. DSD products require a unique inventory management approach because they often have shorter shelf lives, limited shelf space, and frequent deliveries. Effective DSD inventory management is critical to ensure product availability, reduce waste, and optimize the retailer’s profit margins.
The key to successful DSD inventory management is real-time visibility, accurate demand forecasting, efficient order processing, and timely delivery. Retailers need to establish strong partnerships with their DSD suppliers and invest in technology that allows them to track and analyze inventory data in real-time. By doing so, retailers can maximize the benefits of DSD, such as faster product replenishment and increased sales, while minimizing the costs and risks associated with managing DSD inventory.
Best practices for implementing a successful DSD system
1. Develop clear communication processes: Establish clear communication channels between the manufacturer/wholesale distributor and retail stores to ensure accurate and timely delivery of products.
2. Use a direct store delivery solution to optimize delivery routes: Utilize route optimization software to plan the most efficien
t delivery routes, reducing transportation costs and improving delivery times.
3. Train delivery personnel: Provide training to delivery personnel on the products they will be delivering and the direct store delivery process to ensure accuracy and efficiency.
4. Establish partnerships with retailers: Develop strong partnerships with retailers to ensure a seamless and collaborative delivery process.
5. Maintain accurate inventory tracking: Implement a system to accurately track inventory levels to ensure that products are delivered when and where they are needed.
6. Monitor and analyze delivery performance: Regularly monitor and analyze delivery performance to identify opportunities for improvement and make necessary adjustments.
7. Foster a culture of continuous improvement: Encourage a culture of continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and updating DSD processes to ensure they are efficient, effective, and aligned with business goals.
* By implementing these best practices, DSD for distributors and manufacturers can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of their DSD systems and achieve a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Direct Store Delivery Challenges
While Direct Store Delivery (DSD) offers several advantages, it also comes with its set of challenges. Addressing these challenges is crucial for ensuring the smooth functioning of the DSD process. Here are some common challenges associated with DSD:
- Increased Transportation Costs: DSD involves direct deliveries to individual stores, which may lead to higher transportation costs compared to centralized distribution. Managing multiple, smaller deliveries requires efficient route planning to minimize expenses.
- Complex Logistics: Coordinating and managing a decentralized distribution system can be complex. Optimizing delivery routes, managing multiple suppliers, and ensuring timely deliveries to various locations require sophisticated logistics management.
- Inventory Management: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date inventory records becomes challenging when products are delivered directly to stores. Both suppliers and retailers need effective systems for real-time inventory visibility to prevent stockouts or overstock situations.
- Communication Challenges: Effective communication is critical in DSD, but coordinating between suppliers, retailers, and delivery personnel can be challenging. Miscommunications can lead to disruptions in the supply chain and impact product availability.
- Product Quality Control: Ensuring consistent product quality can be more challenging in DSD compared to centralized distribution. Without a centralized warehouse for quality checks, there’s a higher risk of variations in product quality reaching the stores.
- Technology Integration: Implementing and integrating the necessary technologies for real-time data sharing, order processing, and inventory management can be complex. Compatibility issues between systems used by different suppliers and retailers may arise.
- Increased Lead Times: DSD may result in longer lead times for some products, especially if suppliers are delivering directly from manufacturing facilities. This can impact the ability to quickly respond to changes in demand.
- Order Minimums: Suppliers may require retailers to meet certain order minimums for DSD, which can be challenging for smaller retailers with limited storage space or lower sales volumes.
- Dependence on Supplier Reliability: The success of DSD relies heavily on the reliability of suppliers. If suppliers experience disruptions in production or distribution, it can directly impact product availability in stores.
- Training and Compliance: Ensuring that delivery personnel are adequately trained and compliant with regulations can be challenging, especially if there are frequent personnel changes or high turnover rates.
- Limited Product Visibility: Some retailers may have limited control over how products are displayed when delivered through DSD, impacting the overall visibility and attractiveness of the products to consumers.
- Data Security Concerns: The increased use of electronic data interchange and technology in DSD introduces data security concerns. Protecting sensitive information and ensuring secure communication channels is essential.
Successfully navigating these challenges requires a strategic approach, effective technology solutions, and strong collaboration between suppliers and retailers. Regular evaluation and adjustments to the DSD process can help mitigate these challenges and improve overall efficiency.
Efficiency at Your Fingertips: Harnessing the Power of Direct Store Delivery Software
Direct Store Delivery (DSD) software has revolutionized the way businesses manage and optimize their distribution processes. This powerful technology enables manufacturers and distributors to streamline their operations, enhance efficiency, and improve overall customer satisfaction. With DSD software, companies can automate key tasks such as order processing, inventory management, and route planning. Real-time data synchronization ensures accurate and up-to-date information across all levels of the supply chain, allowing for better decision-making and proactive problem-solving.
Furthermore, DSD software provides robust analytics and reporting capabilities, enabling businesses to gain valuable insights into sales performance, product demand, and market trends. By leveraging the power of direct store delivery software, organizations can achieve seamless coordination, reduce errors, minimize costs, and ultimately deliver products more efficiently, resulting in a competitive advantage in today’s fast-paced market.
Direct Store Delivery Trends
Several trends have been shaping the landscape of Direct Store Delivery (DSD). However, keep in mind that the industry is dynamic, and newer trends may have emerged since then. Here are some of the trends that were notable in the DSD space:
- Technology Integration: Increased adoption of technology for better route optimization, real-time tracking, and data analytics. This includes the use of advanced software, GPS tracking, and data-sharing platforms to enhance visibility and efficiency in the DSD process.
- Mobile Solutions: Growing use of mobile solutions for order management, inventory tracking, and communication. Mobile applications help streamline processes and enable real-time updates for delivery personnel and store staff.
- Data Analytics for Demand Forecasting: Leveraging data analytics tools for more accurate demand forecasting. Analyzing sales data, consumer behavior, and market trends helps suppliers and retailers optimize inventory levels and ensure product availability.
- Focus on Sustainability: Increasing emphasis on sustainability in DSD operations, including eco-friendly packaging, energy-efficient transportation, and reducing the overall environmental impact of the supply chain.
- Integration with E-Commerce: Integration of DSD with e-commerce platforms to meet the demands of online shoppers. This involves seamless coordination between in-store deliveries and direct-to-consumer shipments.
- Blockchain for Transparency: Exploration of blockchain technology to enhance transparency and traceability in the supply chain. Blockchain can provide a secure and immutable record of transactions, helping in areas like product traceability and compliance.
- Customization and Personalization: Customizing DSD strategies to meet the specific needs and preferences of retailers and consumers. This may involve personalized product assortments, tailored delivery schedules, and targeted promotional campaigns.
- Rise of Micro-Fulfillment Centers: Consideration of micro-fulfillment centers to support DSD operations. These smaller, automated centers positioned closer to urban areas can enhance efficiency in order fulfillment and reduce delivery times.
- Contactless Delivery and Safety Measures: Accelerated adoption of contactless delivery methods and enhanced safety measures in response to global events like the COVID-19 pandemic. This includes touchless payments, contactless delivery options, and adherence to health and safety protocols.
- AI and Machine Learning for Optimization: Integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) algorithms to optimize various aspects of DSD, such as route planning, demand forecasting, and inventory management.
- Subscription-Based Models: Exploration of subscription-based models in DSD, where consumers subscribe to regular deliveries of specific products. This approach can foster brand loyalty and provide a predictable revenue stream for suppliers.
- Real-Time Promotions and Marketing: Utilizing real-time data and connectivity to implement dynamic promotions and marketing strategies. Suppliers can adjust promotions and pricing in real-time based on factors like inventory levels, demand, and competitor activities.
Keep in mind that the evolution of trends can be rapid, and the current landscape may have seen further developments. Stay updated with industry news and emerging technologies to stay at the forefront of Direct Store Delivery trends.
How to Get Started With Direct Store Delivery?
Getting started with Direct Store Delivery (DSD) can be an exciting move for businesses looking to streamline their supply chain and improve product freshness and availability. Here’s a breakdown of the key steps involved:
1. Plan your DSD strategy:
- Define your goals: Are you aiming for faster delivery, better inventory control, or improved relationships with retailers? Knowing your objectives will help you tailor your approach.
- Evaluate your resources: Do you have the necessary infrastructure, technology, and manpower to handle DSD? This includes things like warehouse space, delivery vehicles, and sales reps.
- Choose your product mix: Not all products are suited for DSD. Focus on high-demand, fast-moving items that benefit from direct delivery, such as perishable goods or consumer electronics.
2. Build relationships with retailers:
- Identify target retailers: Research and select retailers who align with your brand and target audience. Consider factors like store size, location, and product category.
- Negotiate contracts: Agree on terms such as pricing, delivery schedules, and minimum order quantities. Building strong relationships with retailers is crucial for the success of your DSD program.
3. Optimize your operations:
- Invest in technology: Implement a warehouse management system (WMS) and route optimization software to streamline order fulfillment and delivery planning.
- Train your staff: Train your warehouse personnel and delivery drivers on proper product handling, packing procedures, and customer service protocols.
- Monitor and adjust: Continuously track your DSD performance metrics and make adjustments to your strategy as needed. This could involve tweaking delivery routes, optimizing inventory levels, or negotiating new terms with retailers.
Additional tips for success:
- Start small and scale gradually: Don’t try to launch DSD nationwide overnight. Begin with a pilot program in a limited region and gradually expand as you gain experience.
- Focus on customer satisfaction: Make sure your DSD program delivers a positive experience for both retailers and their customers. This means ensuring timely deliveries, accurate orders, and high-quality products.
- Embrace technology: Utilize technology to your advantage to automate tasks, improve efficiency, and gain real-time insights into your DSD operations.
By following these steps and staying adaptable, you can successfully implement a DSD program that benefits your business and your retail partners.
If you would like to learn more about DSD software or DSD route sales software for wholesale distributors, please contact Orders in Seconds for a FREE online demo. – we’re confident you’ll be impressed!
DSD Meaning in Business
In business, DSD stands for Direct Store Delivery, a distribution method where suppliers deliver products directly to retail stores, bypassing traditional distribution centers. This approach offers several advantages, including fresher products, reduced inventory holding costs, and better control over product placement. DSD streamlines the supply chain, enabling faster replenishment cycles and fostering closer relationships between suppliers and retailers.
DSD Meaning in Logistics
In logistics, DSD refers to Direct Store Delivery, a distribution model where products are shipped directly from manufacturers or wholesalers to retail stores. Unlike traditional distribution methods that involve centralized warehouses, DSD eliminates intermediaries, resulting in shorter lead times and reduced inventory holding costs. This approach requires careful coordination between suppliers, carriers, and retailers to ensure timely and efficient delivery to store shelves.
DSD Business Meaning
In the business context, DSD stands for Direct Store Delivery, a distribution strategy where suppliers deliver products directly to retail stores. This approach offers numerous benefits, including faster product replenishment, reduced stockouts, and improved product freshness. By bypassing distribution centers, DSD enables suppliers to have greater control over inventory levels and product visibility, enhancing overall supply chain efficiency.
Direct Store Deliveries
Direct Store Deliveries (DSD) refer to the practice of suppliers delivering products directly to retail stores, bypassing distribution centers. This approach offers several advantages, including reduced handling and transportation costs, shorter lead times, and fresher products on store shelves. Direct Store Deliveries require close collaboration between suppliers and retailers to ensure efficient delivery schedules and inventory management.









